White Mold Vs Black Mold: Understanding The Risks and Differences
Mold is a common household issue that can pose serious health risks if not properly addressed.
We will explore the differences between white mold and black mold, including their appearance, growth patterns, and associated health risks.
Learn about the risks of mold exposure, such as respiratory issues, allergic reactions, and skin irritation.
Discover tips on how to identify and get rid of white mold versus black mold through prevention methods, and professional mold removal services.
Let’s learn how to protect our health and homes from the harmful effects of mold.
Key Takeaways:
- Mold can be harmful to our health and cause respiratory issues, allergic reactions, and skin irritation.
- White mold and black mold may look similar, but they have different growth patterns and health risks.
- Prevention is key in avoiding mold growth, but if mold is present, professional mold removal is the safest and most effective option.
What is Mold?
Mold is a type of fungus that grows in moist environments and reproduces by releasing spores into the air.
Characterized by its fuzzy appearance and musty odor, mold thrives in areas with high humidity and poor ventilation. Once spores find a suitable environment, they quickly multiply, forming colonies on various surfaces. These resilient organisms can spread rapidly, posing health risks to individuals exposed to them. The presence of excessive moisture, organic matter, and darkness creates the perfect breeding ground for mold. Without proper preventative measures, such as controlling indoor humidity levels and promptly addressing leaks, mold infestations can become challenging to eradicate.
What are the Different Types of Mold?

Mold comes in various types, including the infamous black mold (Stachybotrys chartarum) and white mold, each with different characteristics and risks associated with them.
White Mold
White mold is a type of fungus that thrives in high humidity environments and is commonly found on surfaces like drywall and ceilings.
One of the distinct characteristics of white mold is its powdery or cotton-like appearance, often mistaken for efflorescence or dust accumulation. It prefers damp and humid conditions, making it a common issue in areas with high moisture content such as bathrooms, basements, and areas affected by water leaks.
White mold can be especially damaging to materials like drywall, where it can cause discoloration, deterioration, and a musty odor. If not addressed promptly, it can spread rapidly and compromise the structural integrity of buildings.
Black Mold
Black mold, also known as Stachybotrys chartarum, is a toxic type of mold commonly found in damp areas like HVAC ductwork, capable of producing harmful mycotoxins.
It thrives in environments with high humidity and moisture, making HVAC systems an ideal breeding ground for its growth. The presence of black mold in ductwork can lead to serious health issues if left unchecked, as inhalation of its spores releases dangerous mycotoxins into the air. Exposure to these toxins can trigger respiratory problems, allergic reactions, and even neurological issues in some individuals. Proper ventilation, moisture control, and regular maintenance are essential in preventing the spread of black mold within HVAC systems.
What are the Risks of Mold Exposure?

Exposure to mold can lead to a myriad of health risks, including respiratory problems, allergies, neurological issues, compromised air quality, and even structural damage in buildings.
Respiratory Issues
Respiratory issues are common health risks associated with mold exposure, manifesting as breathing difficulties, allergic reactions, and exacerbation of existing respiratory conditions.
One of the most common respiratory problems linked to mold exposure is asthma, a chronic condition characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Inhalation of mold spores can trigger asthma attacks, leading to wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. Mold exposure can worsen symptoms of chronic bronchitis, causing increased mucus production and persistent cough.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to mold exposure can range from mild symptoms like sneezing and skin irritation to severe conditions that impact overall health, varying based on the individual’s sensitivity.
For some people, exposure to mold spores can lead to severe respiratory distress and asthma attacks, posing significant health risks. Inhaling mold spores can trigger inflammation in the airways, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Additionally,
- White mold
- and black mold, such as Stachybotrys chartarum, can elicit different allergic responses based on the toxins they release. While white mold spores may cause milder symptoms like headaches and nasal congestion, black mold exposure can result in more severe reactions like nausea and fatigue.
Recognizing the signs of mold allergies is crucial in preventing long-term health complications and addressing any underlying issues promptly.
Skin Irritation
Skin irritation is a common allergic response to mold exposure, characterized by rashes, itching, and redness on the skin, with different mold types like white mold and black mold potentially causing varying dermatological reactions.
White mold-induced skin irritation typically presents as mild redness and itching on the affected areas, while black mold exposure can lead to more severe symptoms such as blistering, inflammation, and in some cases, skin infections. It is essential to differentiate between these reactions to tailor appropriate treatment plans for individuals experiencing mold-induced skin irritations.
How to Identify White Mold vs Black Mold?

Distinguishing between white mold and black mold involves considering factors like color, texture, and location of the mold growth, aiding in accurate identification and appropriate remediation measures.
Color
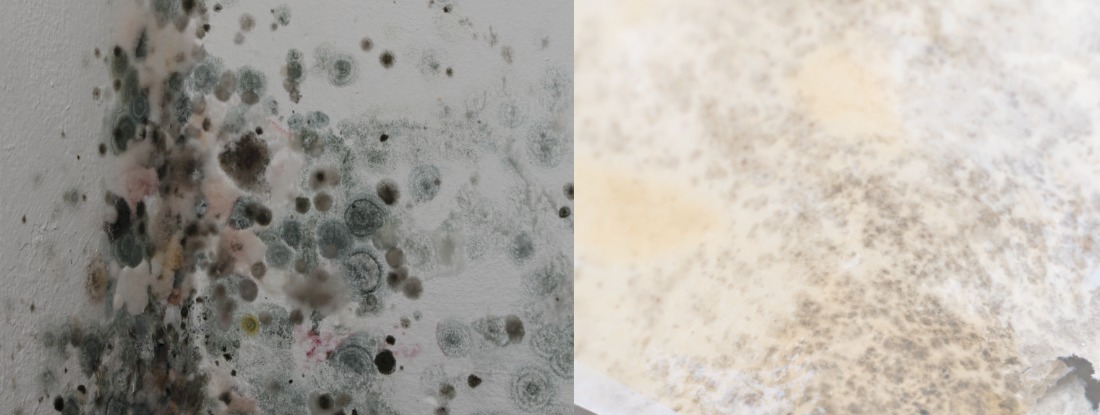
Color is a crucial aspect in distinguishing between white mold and black mold, with white mold typically appearing as light-colored patches and black mold exhibiting dark or greenish hues on surfaces.
Understanding the significance of color in mold identification plays a vital role in effectively managing mold growth. Differentiating between white and black mold based on color variations and patterns is essential for accurate recognition and appropriate remediation strategies. White mold often presents itself as powdery or fuzzy spots, usually light in color, while black mold tends to be slimy with dark or greenish shades. By recognizing these distinct color characteristics, individuals can promptly address potential mold issues, safeguarding indoor environments from harmful mold infestations.
Texture
Texture differences play a role in discerning white mold from black mold, as white mold often has a fuzzy or powdery texture, while black mold appears slimy or grainy, aiding in the identification process based on tactile characteristics.
Texture plays a crucial role in differentiating white mold and black mold. When touched, white mold is often described as fuzzy or powdery, resembling cotton or flour. On the other hand, black mold gives off a slimy or even grainy sensation, reminiscent of grease or wet sand.
These variations in touch are key factors in distinguishing between the two types of mold. Being able to identify the textural differences helps in not only recognizing the type of mold but also in understanding their growth patterns and possible risks associated with them.
Location
The location of mold growth can provide valuable clues in differentiating between white mold and black mold, with specific areas like damp basements favoring white mold and moisture-rich environments supporting black mold proliferation.
White mold tends to thrive in areas with high humidity levels, such as bathrooms and kitchens with poor ventilation, offering a fluffy, cotton-like appearance. On the other hand, black mold thrives in dark, damp corners like attics or crawl spaces, often appearing slimy and toxic.
Health Risks associated with white mold exposure include allergic reactions, respiratory issues, and headaches, while black mold exposure can lead to severe respiratory problems, skin irritations, and in severe cases, neurological issues. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective mold management and remediation.
What are the Differences between White Mold and Black Mold?
White mold and black mold exhibit differences in their appearance, growth patterns, and associated health risks, making it essential to understand the distinctions between the two mold types for effective remediation strategies.
Appearance
The appearance of white mold differs from black mold in terms of color, texture, and overall visual characteristics, providing visual cues that assist in distinguishing between the two mold types.
White mold typically appears as a powdery, fluffy substance with a light, almost cotton-like texture, often covering a larger surface area in a uniform manner. On the other hand, black mold tends to be slimy or greasy in texture, presenting itself in small patches or spots that may be mistaken for dirt or grime at first glance.
Color wise, white mold usually ranges from bright white to a light grey, while black mold is dark green or black, sometimes with hints of dark brown or grey. Differences in appearance such as these are crucial in accurately identifying and addressing mold infestations.
Growth Patterns
White mold and black mold exhibit distinct growth patterns influenced by factors like location, texture preferences, and environmental conditions, shaping their spread and impact on surfaces.
White mold tends to thrive in damp and humid environments, particularly on decaying organic matter like wood and paper, while black mold demonstrates a preference for wet surfaces such as bathroom walls and ceilings.
The texture of the surface also plays a role in the growth of these molds, with white mold commonly seen on softer surfaces like fruits and vegetables, whereas black mold can adapt to grow on a wider range of materials, including drywall and fabrics.
The environmental requirements for white mold and black mold differ, with white mold requiring higher moisture levels for optimal growth, whereas black mold can survive in lower humidity conditions but still proliferates in areas with water leaks or condensation.
Health Risks
White mold and black mold pose distinct health risks to individuals, with white mold potentially triggering respiratory problems and black mold impacting neurological health, necessitating prompt remediation efforts for safety.
White mold exposure can lead to a range of respiratory issues such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, making it particularly dangerous for individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions.
Neurological issues associated with black mold exposure are concerning, as symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, and even memory loss, affecting both short-term and long-term brain function.
Aside from these specific health concerns, mold exposure can also weaken the immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to other illnesses.
How to Get Rid of White Mold vs Black Mold?
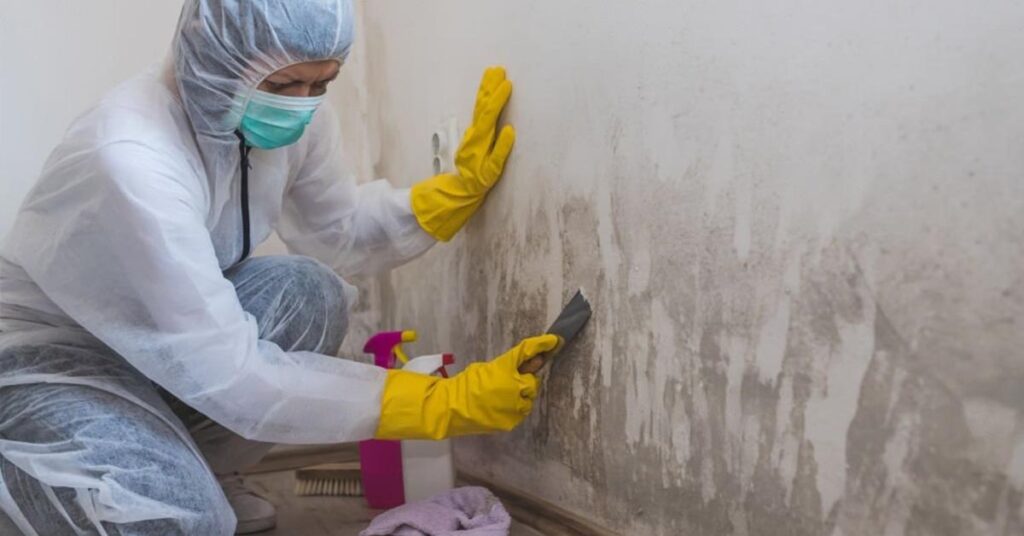

Eliminating white mold and black mold involves implementing preventive measures, undertaking DIY remediation efforts, or seeking professional mold removal services depending on the severity of the infestation and the expertise required for safe mold eradication. Being aware of the difference between mold remediation and mold removal can also help.
Prevention Methods
Preventing white mold and black mold growth involves controlling moisture levels, improving ventilation, and maintaining indoor air quality to create inhospitable conditions for mold proliferation, reducing the risk of infestations.
Prevention Methods are essential to curb the development of white mold and black mold.
- Proper ventilation, such as installing exhaust fans in high moisture areas like bathrooms and kitchens, can help expel humid air, thus reducing the dampness that mold thrives on.
- Monitoring and controlling indoor Air Quality through regular HVAC maintenance, using HEPA filters, and ensuring adequate air circulation can also hinder mold growth by promoting a dry and well-ventilated environment.
DIY Remediation
DIY remediation for mold is not recommended but involves methods like cleaning with fungicidal solutions, removing affected materials like drywall, and addressing underlying issues such as efflorescence to eradicate mold growth and prevent recurrence.
One crucial step in DIY mold removal is to ensure proper ventilation during the cleaning process to prevent further mold spores from spreading in the air. Apart from using fungicidal cleaners, natural alternatives like vinegar and baking soda can also be effective in combating mold.
Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and masks, is essential when dealing with mold to avoid exposure to harmful spores.
Thoroughly drying the affected area after cleaning can help prevent mold re-infestation. Considering professional assistance if the mold infestation is extensive is always a wise decision.
Professional Mold Removal
Professional mold removal services offer expertise in safely eliminating white mold and black mold infestations, utilizing advanced techniques, containment procedures, and restoration measures to address mold growth in challenging areas like HVAC ductwork or structures.
Removing mold efficiently requires more than just wiping the visible areas. Professional mold removal experts undergo specialized training to identify hidden mold, assess the extent of the damage, and use advanced techniques to eliminate the source of the mold. By following strict containment protocols, they prevent the spread of mold spores to other parts of the property.
Structural restoration is a crucial aspect of the mold removal process. After eliminating the mold, professionals focus on repairing any structural damage caused by the infestation. This ensures the long-term integrity and safety of the building, providing a comprehensive solution to mold-related issues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the distinctions between white mold and black mold is crucial for effective identification, mitigation of health risks, and implementation of appropriate remediation measures tailored to each mold type’s characteristics and associated dangers.
White mold, often a powdery substance, thrives in damp environments with organic materials, while black mold, commonly slimy or fuzzy, prefers areas with high moisture content such as bathrooms and basements. The health risks vary, with white mold typically causing respiratory issues and allergies, and black mold being more toxic and potentially leading to severe health problems.
When dealing with white mold, improving ventilation and reducing humidity levels are key for prevention. On the other hand, black mold removal requires professional intervention due to its toxicity. Proper protective gear and containment measures are essential in both cases to prevent mold spores from spreading during the remediation process.
Frequently Asked Questions About White Mold Vs Black Mold
What is the difference between white mold and black mold?
White mold and black mold are two types of fungi that can grow in households. While both can be harmful, they have distinct differences in appearance and behavior. White mold is typically fuzzy and has a light color, while black mold is slimy and has a dark color. Additionally, white mold tends to grow on plant-based materials, while black mold can grow on a variety of surfaces.
What are the health risks associated with white mold and black mold?
Both white mold and black mold can cause health problems when inhaled or touched. White mold can lead to respiratory issues, such as coughing and wheezing, while black mold can cause more serious issues like allergic reactions and even neurological problems. It is important to address mold growth in your home to avoid these health risks.
How can I identify whether I have white mold or black mold in my home?
The appearance and location of the mold can help determine which type it is. White mold is often found on organic materials like wood or plants, while black mold can grow on a variety of surfaces, including drywall, ceiling tiles, and carpets. You can also have a professional mold test done to accurately identify the type of mold present.
Can I remove white mold and black mold myself?
It is not recommended to try and remove mold yourself, especially if it covers a large area or is in hard-to-reach places. Mold removal can be dangerous and should be left to trained professionals who have the necessary equipment and knowledge to safely remove and dispose of the mold.
What steps can I take to prevent white mold and black mold growth in my home?
To prevent mold growth, it is important to control moisture levels in your home. Fix any leaks or water damage immediately, keep humidity levels below 50%, and ensure proper ventilation in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms and kitchens. Regularly inspect and clean areas that are susceptible to mold growth.
Is white mold or black mold more dangerous?
Both white mold and black mold can be harmful, and the severity of their health risks depends on various factors such as the individual’s sensitivity and the amount of exposure. It is important to address any mold growth in your home promptly, regardless of its color, to avoid potential health problems.